What is a Stroke?
A Stroke: What Is It?
A stroke, also called a “brain attack,” happens when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. When blood flow is stopped the brain tissue does not get enough blood and oxygen to survive. Brain cells can die, causing permanent damage.
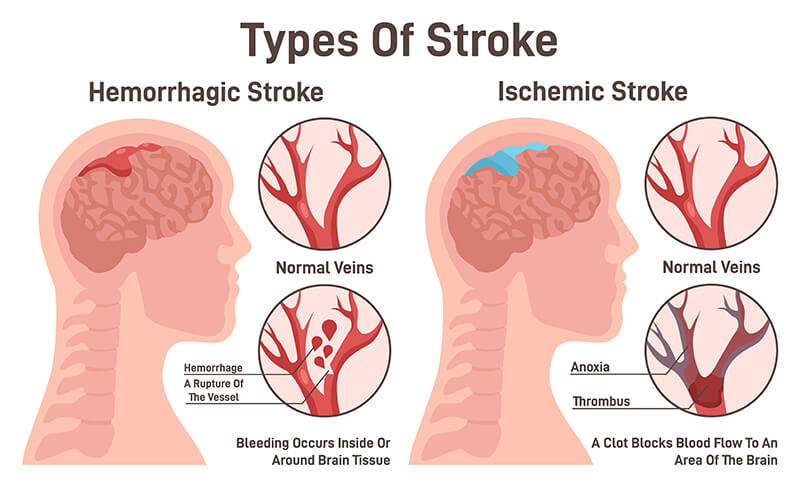
Hemorrhagic Stroke is caused by the rupture of a blood vessel either inside or around brain tissue.
Ischemic Stroke is caused by a blood clot or clogged blood vessels due to atherosclerosis that cuts off blood flow to an area of the brain.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA or mini-stroke) is the same as a stroke, but the symptoms last a short time. You get stroke symptoms because a clot is blocking the blood supply in your brain. When the clot moves away, the stroke symptoms stop. About 1 in 3 people who has a TIA will eventually have a stroke, with about half occurring within a year after the TIA.